
This page is part of the GeneWarrior Documentation. Go to the main site of GeneWarrior
See also how to translate DNA to protein.
Translation is the process where ribosomes create proteins by decoding nucleotide sequences. A single amino acid is encoded by three nucleotides (codon). The translation step from codon to amino acid (which codon encodes which amino acid) is determined by the genetic code (or translation table) that may slightly differ among different species.GGGTTT can either be GGG, GGT or GTT, depending on whether the codon starts on position 1,2 or 3. These are called the three reading frames, and they result in three distinctly different protein sequences.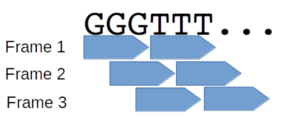
AUG (the start codon). Furthermore, translation is terminated by a stop codon.
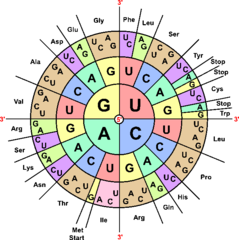
However, depending on the phylogenetic clade there are some differences in the code, which mostly apply to start and stop codons.
For example, in the Genetic Code of the Mitochondrion, the TGA-codon encodes a tryptophan (W) instead of the stop codon in the standard genetic code.
To see the complete list of all currently known genetic codes, see NCBI's list.
For more information about the biological details of the translation process, see the well written and illustrated article from Nature.com.
See the Tutorial on how to translate DNA to protein.